Contents
INTRODUCTION
At the beginning of March I was lucky to take part in Scrum Master training held by Gabrielle Benefield in London. For me it was a first milestone to become a Certified Scrum Master, improve my knowledge about scrum methodology and gain new experiences. I am happy that after the course I have the possibility to implement my new knowledge into Vaimo’s teams. I decided to summarise my training and share the most important facts and skipping basic knowledge about Scrum Mastering. Happy reading! Let’s start with a little bit of theory.
CYNEFIN AND MOBIUS
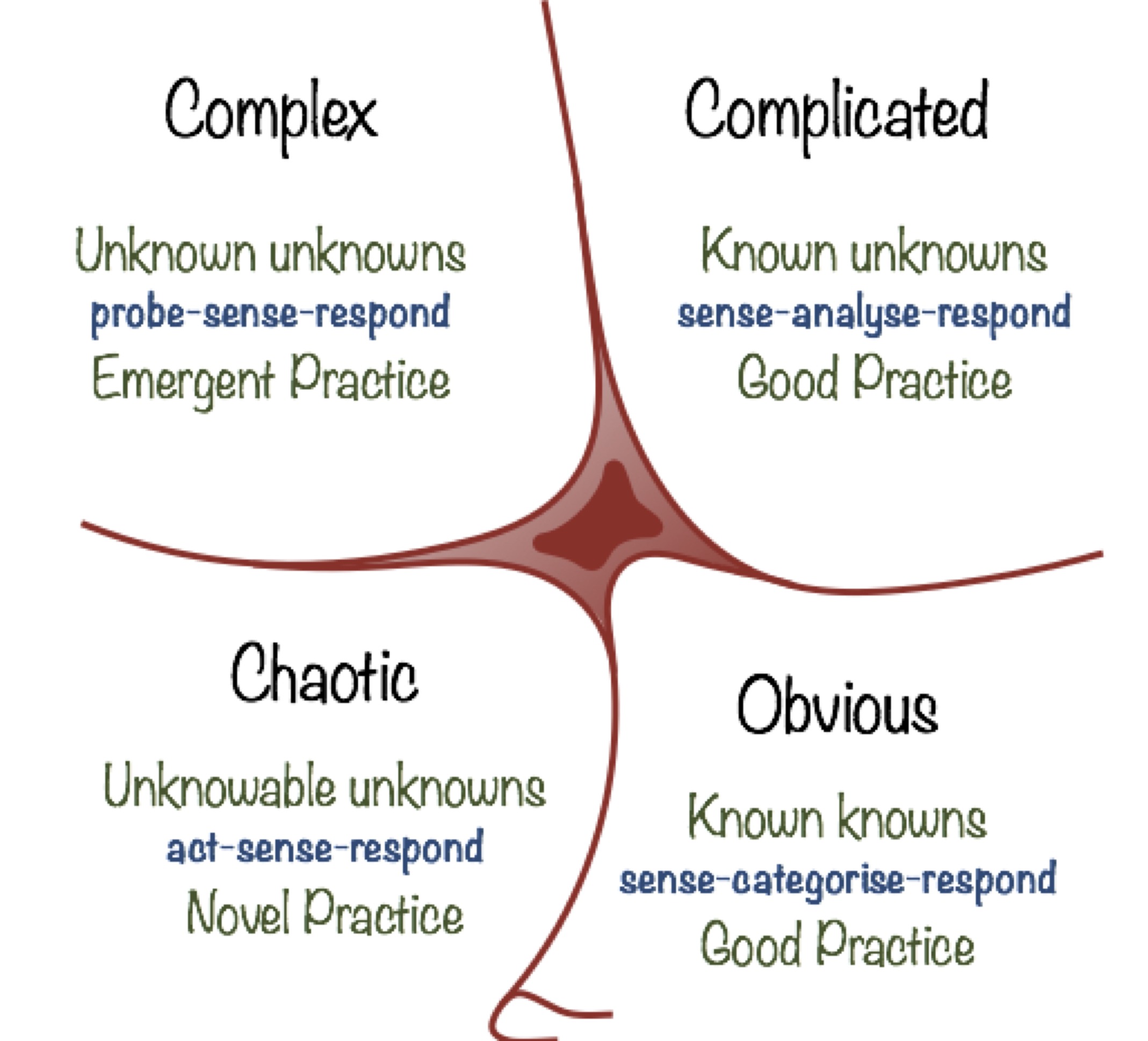
Cynefin
The cynefin graph represents different types of tasks.
- Simple – cause and effect are obvious and known.
- Complicated – cause and effect requires analysis and expert knowledge.
- Complex – cause and effect can be fully perceived in retrospect, not in advance.
- Chaotic – there is no relationship between cause and effect.
Scrum is an empirical framework which focuses on complicated and complex tasks.
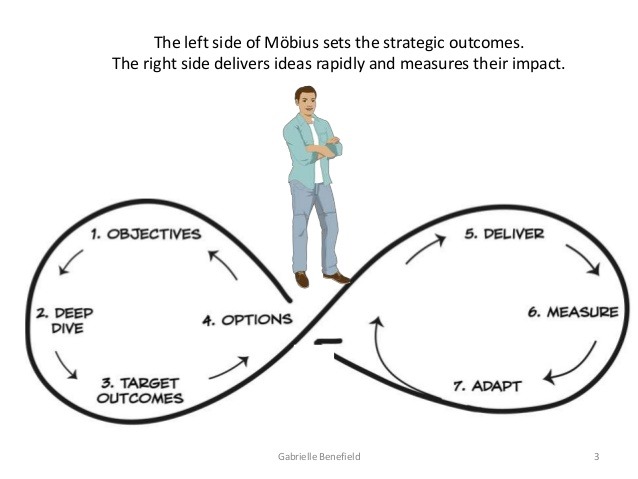
Mobius loop
The mobius loop represents scrum workflow. The right side of the graph includes research, experiments, implements and measure. We have to remember that the most important part is an outcome, which is a value for the scrum team. The output includes features which are delivered by the team, however only outcome is valuable for the scrum process. More features doesn’t mean customer value! The scrum team should focus on features which are important from a business point of view – that’s our customer value, that’s our goal.
HOW TO UNDERSTAND SCRUM
Ball point game
One of our first exercises during the course was ball point game. I believe it is one of the best examples that allows us to understand scrum’s rules. Please see description below.
During our game we understood several points:
- Smaller teams are much more effective than bigger teams.
- The estimation for the couple of first sprints is totally wrong, with experiences the estimation gets closer to real results.
- The retrospective meeting has a huge impact on the sprints and helps increase results dramatically.
- Don’t discuss solutions too long, just try it for a couple of sprints, if it works, implement it.
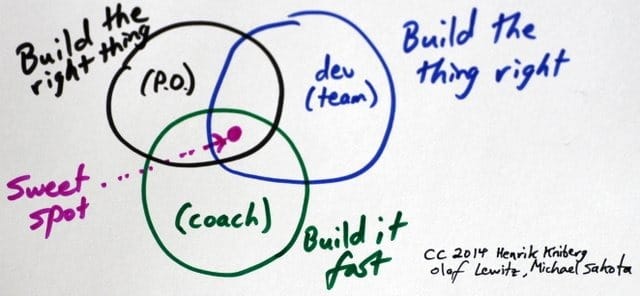
Find a balance
The graph below illustrates responsibilities between scrum team members.
- Product Owner has to make sure that the development team builds the right features.
- Development team has to make sure that the features are built in the right way.
- Coach (Scrum Master) has to remove all impediments in order to make process run more smoothly.
The idea of a scrum process is to find balance and meet each other in the middle – the sweet spot.
PRODUCT OWNERSHIP AND MOTIVATION
Product ownership
The video above explains the whole scrum process. I would like to draw attention to some important points.
- Overwork – I believe we can find this issue in most of our teams. It is a really important point because it causes problems in the team. The team members are unmotivated and less effective. It has to be understood by Product Owners and Scrum Master.
- Say “NO” – Product Owners should say “NO” to customers. It is obvious that clients will try to get as many new features as possible in a short amount of time. In order to finish a project with success, the Product Owner should say “NO” to most of the propositions and choose only the most valuable for the customer.
- Communication between team members and stakeholders – Scrum highly recommends communication between all team members, that means developers should have direct contact with the client. In this way we avoid misunderstanding.
- Task prioritisation – during the planning meeting we should prioritise the tasks in specific way.
- First choose tasks which are the most valuable for the business and the smallest ones. These will have the biggest impact for stakeholders.
- Then choose valuable but bigger ones, which take more time.
- At the end choose the rest of them. We have to always remember to deliver the most valuable tasks for our clients in the short time.
- Balance between short and long term tasks – during our workflow we have to find balance between urgent fixes which have to be done immediately and big features.
Motivation
The video above illustrates the motivational aspect of the work. I would like to mention, once again, about the most significant points in the video.
- AUTONOMY – self-direction is a powerful tool to increase engagement.
- MASTERY – allows people and helps them to be a master.
- PURPOSE – I believe this is the most powerful aspect of life.
SCRUM GLOSSARY AND SCRUM MASTER ROLE
During the whole of our training we had Sprint Backlog visible on the wall where we tracked our progress by moving tasks to the specific columns. I think it is a great idea for scrum master training. From the early beginning we learnt basic scrum processes.
Scrum Glossary
One of the tasks on our Sprint Backlog was Game of Scrum where we were working on the Scrum Glossary.
- First day of the sprint doesn’t need to be a Monday! Choose a day that fits your organisation. Some of the teams prefer to start the sprint on Tuesday or Thursday.
- Let’s make clear responsibility of each of team members.
- Scrum Master makes sure that the scrum methodology is understood and he is responsible for coaching the team. He makes sure that the meetings are fitted timeboxes and removes all impediments.
- Product owner is responsible for managing Product Backlog and overall product success.
- Development team is a cross-functional team, they are self-managed and self-organised. The team works with Sprint Backlog where they can add items, remove and move.
- As we can see, very often we can meet tasks without the correct user story, it is worth a reminder that User Story answers 3 questions – Who, What and Why. Moreover Acceptance criteria are important for satisfaction from business perspective.
- Definition of Done should be defined by each of the team, it has to include work of each of the team members.
- Sprint Backlog is managed by the development team. Team members can add, remove, move items in order to achieve sprint goal. Product backlog is managed by Product Owner. During the planning meeting, the development team decides which item can be delivered in the next sprint, then these items are divided into Sprint Backlog tasks which are created by the development team.
- Everyone can join DS, however only the Scrum team can speak.
- Sprint review has to be an honest meeting. Only features which are done regarding to Definition of Done can be presented. The most important part of the meeting is feedback.
- Scrum of Scrum shouldn’t be just meeting of Scrum Masters. Every week different a team member should participate in the meeting. They should share their experiences and challenges.
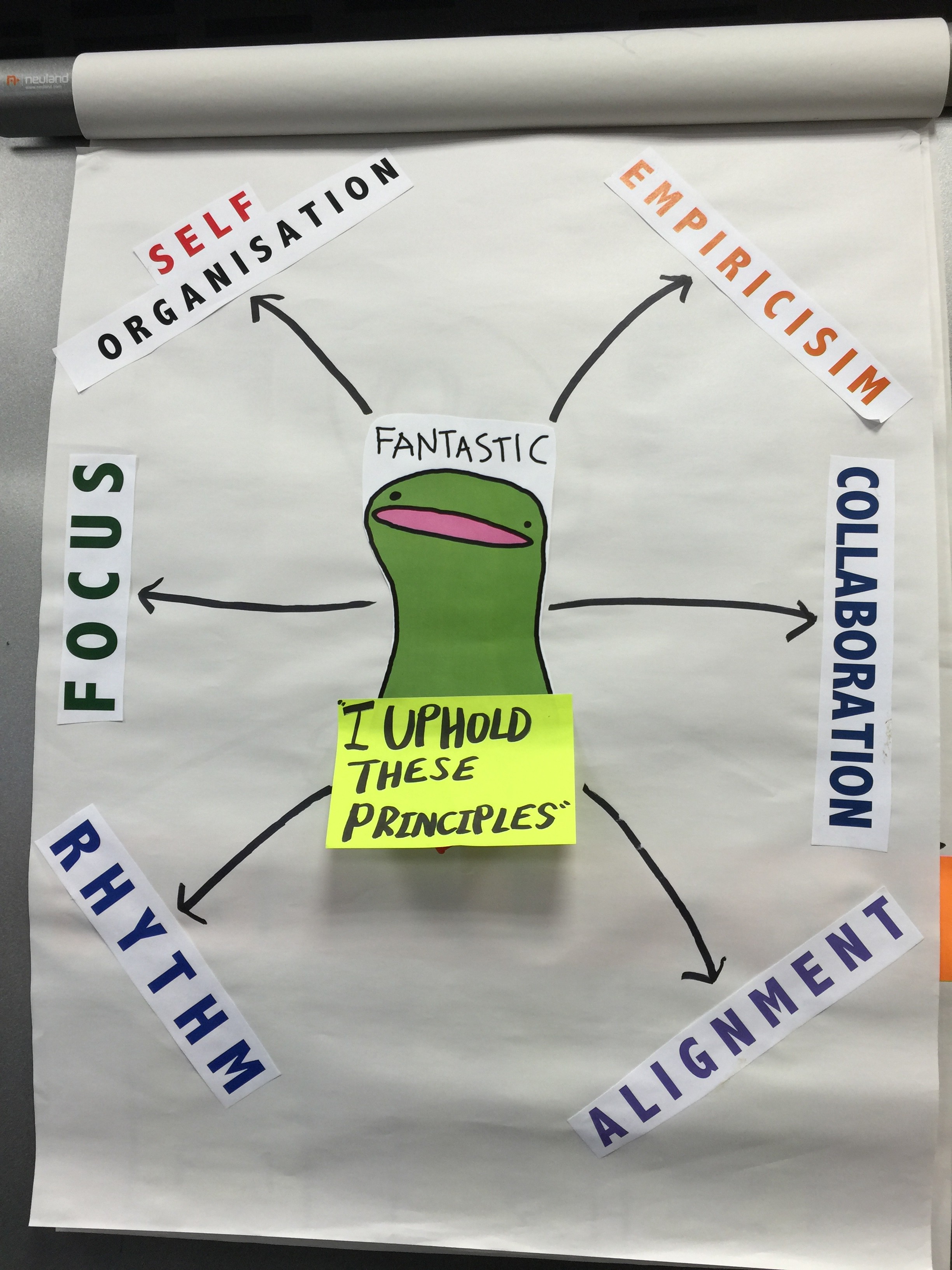
Scrum Master Role
Please, see the picture below. It illustrates features of perfect Scrum Master. In the middle of the picture, there is a yellow card, under this card there is a word – TRUST. It is the main point of scrum mastering – trust – believe that the intention of each team member is good.
ESTIMATION AND BUDGETING
Estimation
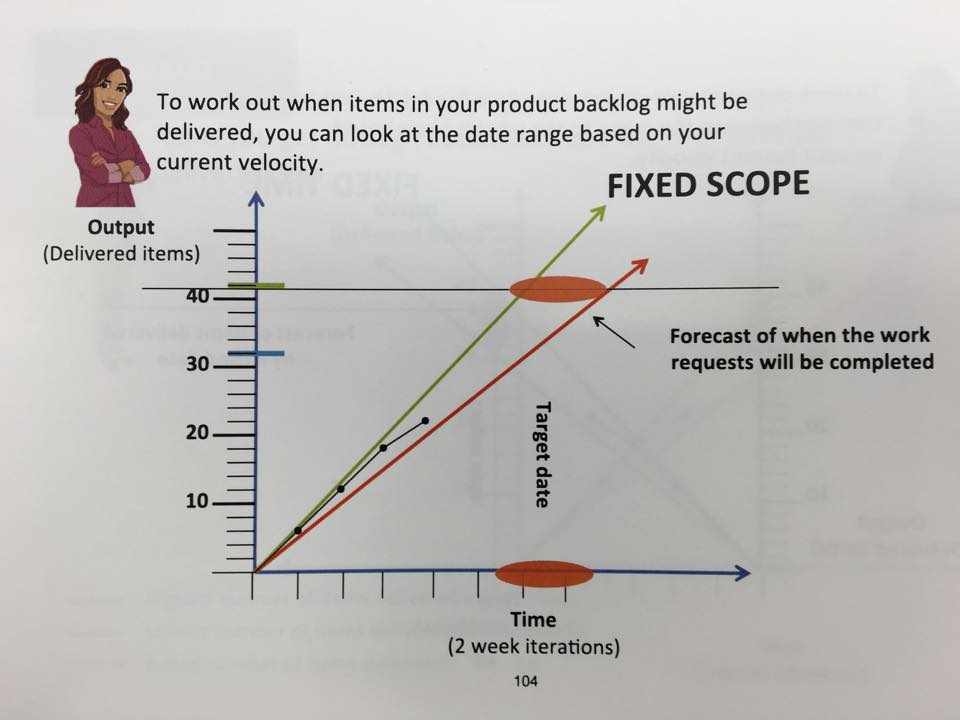
The pictures below show some advice regarding to estimation and budgeting. I would like to just mention that Estimation and Budgeting is not a part of Scrum, that’s why scrum gives some advices but not rules. We have to remember that we should estimate tasks regarding to Definition of Done.
One of the methods that was mentioned during our course, was to ask the team if a specific task can be delivered in the next sprint. The answers could be – YES, NO, MAYBE. That’s all. Scrum estimation should only answer if specific tasks can be delivered in the next sprint. Maybe for some of our teams, this method can work and be more efficient.
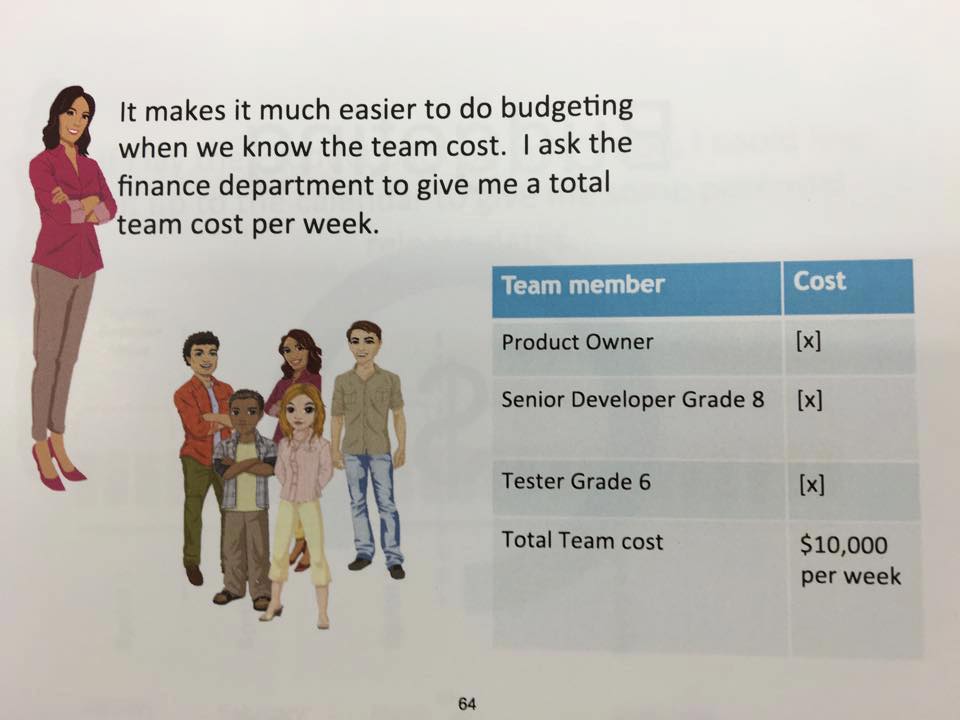
Budgeting
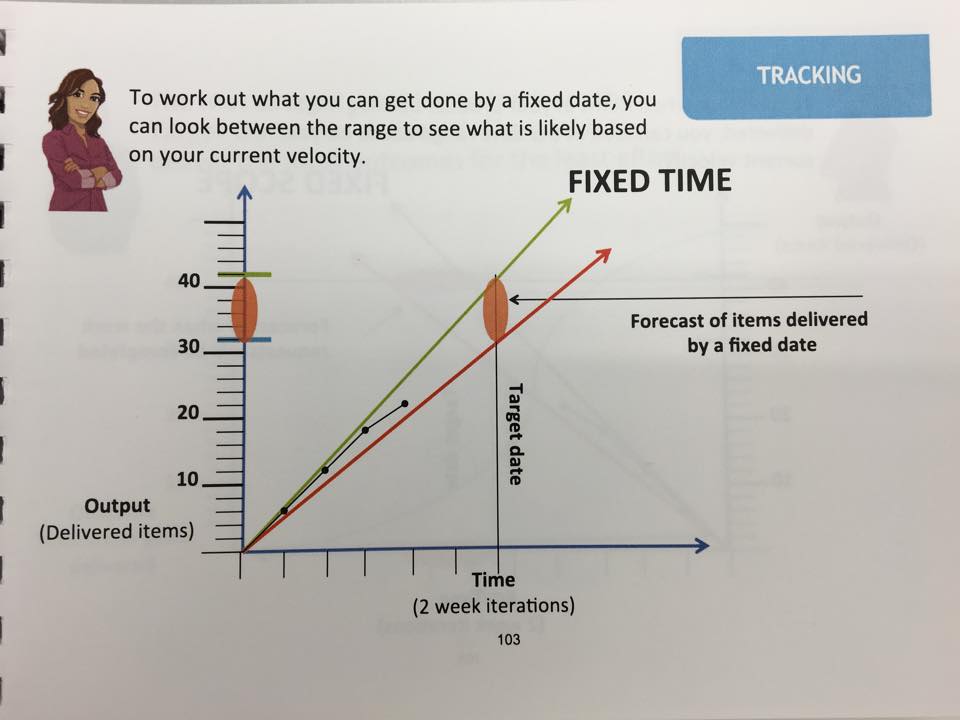
TRACKING
The burn-up can be a really efficient tool for Product Owner and Stakeholders.
The green line is the highest number of items delivered per iteration.
The orange line is the lowest number of items delivered per iteration.
The black line is the actual number of items delivered.
CANCELLATION AND FIRES
Cancellation
I am not sure if it is clear that the sprints can be actually cancelled.
There are some steps which should be implemented:
- Innovate – Can we do this a different way?
- Delegate – Can anybody else help?
- Descope – Can we remove something?
- Abort – Do we have to cancel the Sprint?
Fires
How many times didn’t you achieve your goal because of urgent issues and blockers? Please, see some advises below.
CHALLENGES

CONCLUSION
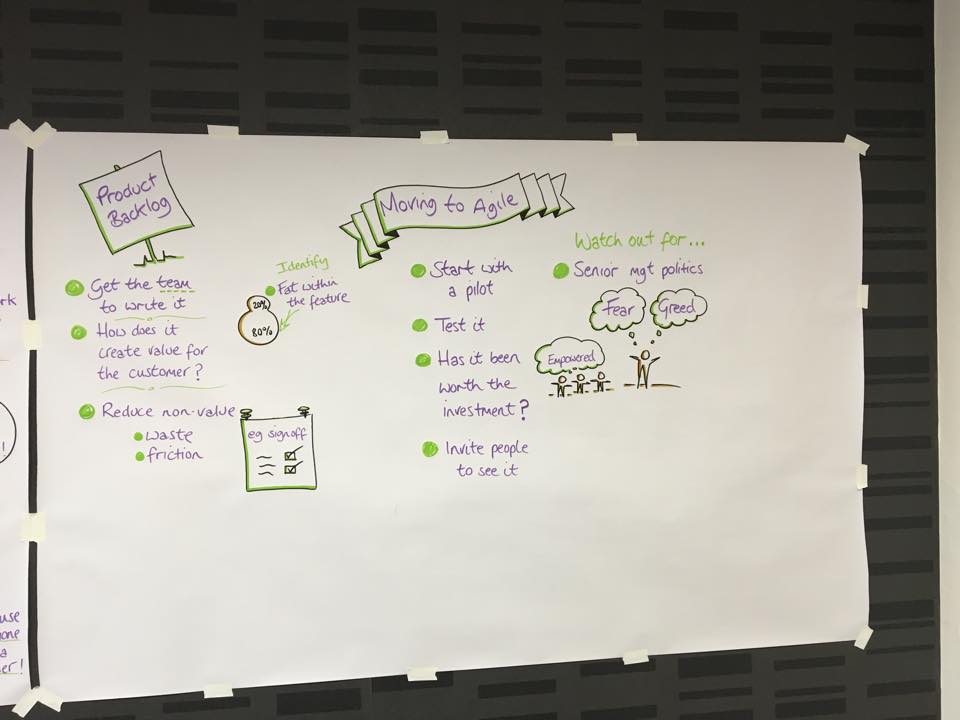
During our course we had a guest who was drawing the most important sentences about scrum process. It think it is a pretty cool summary of our training.
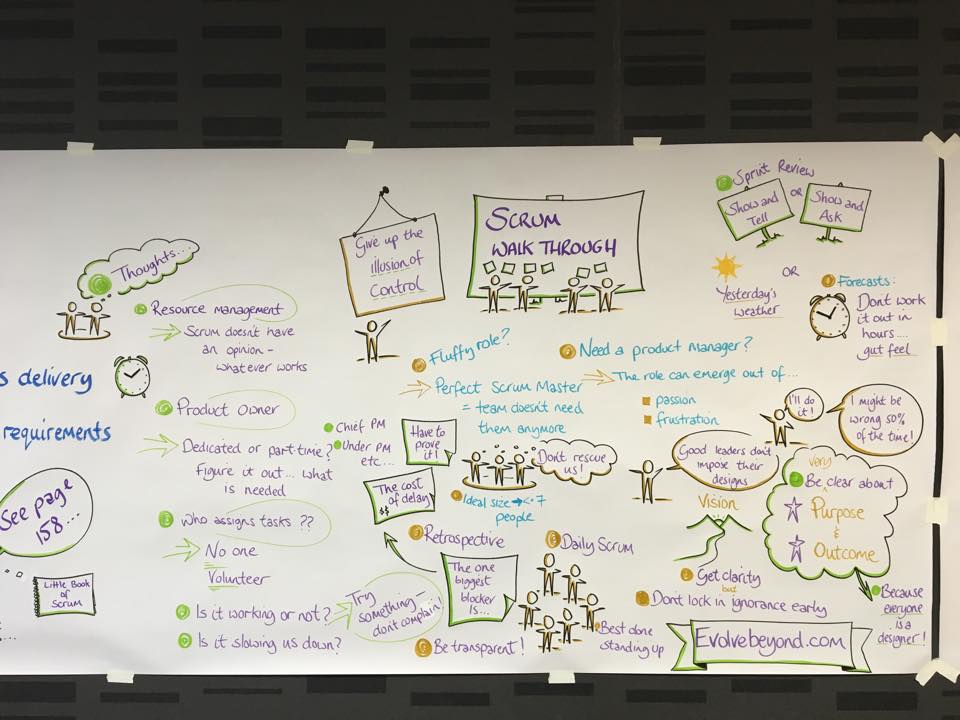
Also I have some of my favourite points. Please, see below.
“Give up the illusion of control”
“Run experience”
“Scrum doesn’t care, it is working for you? If so, do it!”
“Focus on the customer’s problem, don’t miss the problem during the whole process. First of all, find quick and simple solutions in urgent situations”
“Remember to find a balance, meet the customer’s needs, however remember that the company needs to earn in order to meet their customer’s needs”
“Fire in the stomach, ice in the head!”
Finally, the last thing we did during our course, we took part in a small exercise. Please, see the cases below and try to find a solution and answer the question – What a Scrum Master should do in this kind of situation? Feel free to add your answers in the comments or contact me to discuss it with me.
Good luck!
Editor – Natasha Jay O’Neil, please contact Natasha directly for queries related to her services.
Zaneta loves challenges so deciding about career path she has chosen typical male industry. Woman who codes. Every 1-2 years she lives in different part of the world. Gym dates is something what she specialised in. Healthy lifestyle, extreme sports and motorbikes have stolen her hear years ago.